|
The "5Es of Economics" are not from
the textbook. I borrowed the concept (with many
modifications) from another textbook many years ago. I
believe it concisely explains the purpose of economics.
Also, it begins to introduce students to the economic way of
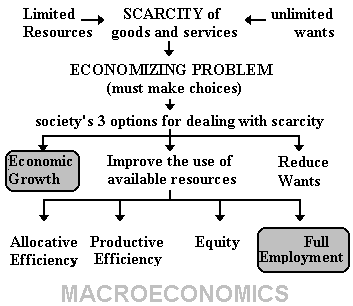
thinking. The economic problem that we all face, that all
countries face, that the world faces, is SCARCITY. Economics
is the study of how we can reduce scarcity. What I like
about the 5Es model is that it shows us that there are only
five ways to reduce scarcity. Only five. I call them the
"5Es" of economics.
For each of the 5Es:
(1) learn the definition,
(2) understand examples, and
(3) most importantly, know how they reduce scarcity and help
to increase society's satisfaction.
This is where you learn that it may
be good when the price of plywood increases greatly as the
result of a hurricane. And why it might be good when
Coca-Cola lays of one fifth of its workforce. Or, that the
price of gasoline may be too low. Really!
In this MACROeconomics course we will
focus on Economic Growth and Full Employment. Efficiency,
efficiency, and equity are the focus of my MICROeconomics
classes and few economists study "Reducing Wants". The
overall goal of economics is to REDUCE the SCARCITY of goods
and services. Economic growth and full employment are two
(of five) ways to do this.
Pay close attention to the new
definition of economic growth presented in the online
reading. It is different from what you might hear in a news
report. Also, pay attention to HOW such economic growth is
achieved:
- finding more resources,
- getting better resources,
- and inventing better technology.
This type of economic growth involves
INCREASING THE POTENTIAL of the economy to produce goods and
services.
Full employment helps an economy
ACHIEVE ITS POTENTIAL by using all of its resources.
Again, notice the slightly different definition than is
commonly used for full employment. We are not just talking
about labor, but ALL available resources.
There are three issues that
macroeconomics studies: (1) unemployment - UE, (2) inflation
- IN, and (3) economic growth - EG, (UE, IN, and
EG).
|