|
In Lesson 2a we learned about the
following Structural Adjustment Policies and the following
characteristics of capitalist economies:
Structural Adjustment
Policies:
- Privatization
- Promotion of Competition
- Reduced Role of Government
- Removing Price Controls
- FREER TRADE and Convertible Currency
- Foreign Investment
Characteristics of Capitalist
Economies:
- private property
- freedom of enterprise and choice
- role of self interest
- competition -
- markets and prices
- limited role for government
In this lesson we will study
trade.Trade increases competition and helps the world's
economies achieve PRODUCTIVE EFFICIENCY (producing at a
minimum cost by using resources where they are best suited).
Therefore it is an important concept to study in any
introductory economics course.
We will learn that trade based on
COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE can help the world PRODUCE MORE from
the same amount of resources. Trade allows all
countries to consume beyond their production
possibilities (point E on the graph below).
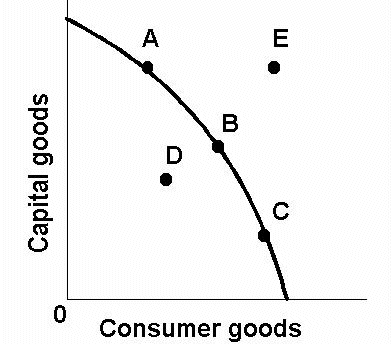
How is that possible?
We will also learn that even if a
country is better at producing all products, it is still
possible for it to come out ahead if it specializes and
trades with other (less productive) countries.
How is that possible?
That is why there has been a trend
over several decades of the world moving to ward freer and
freer trade.
|